Dog shots are an essential aspect of responsible pet ownership. Vaccinations protect dogs from contracting and spreading diseases, some of which can be fatal. However, the cost of these shots can vary depending on a variety of factors, such as the location, the type of vaccine, and the veterinarian.

The price of dog shots can range from $20 to $150 per vaccine. This cost can add up quickly, especially if a dog requires multiple shots. The most common vaccines required for dogs include rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and adenovirus. Some veterinarians may also recommend additional vaccines based on a dog's lifestyle and risk factors. It is important for pet owners to discuss the necessary vaccines with their veterinarian and understand the associated costs.
Understanding Dog Vaccinations
Dog vaccinations are an essential part of responsible pet ownership. They help protect dogs from various diseases and illnesses that can be dangerous and even fatal. Understanding the different types of vaccines and their purposes can help pet owners make informed decisions regarding their dog's health.
Core vs. Non-Core Vaccines
Core vaccines are those that are recommended for all dogs regardless of their lifestyle or environment. These vaccines protect against diseases that are widespread, highly contagious, and have a high risk of severe illness or death. The core vaccines for dogs include rabies, distemper, parvo, and adenovirus.
Non-core vaccines, on the other hand, are recommended for dogs based on their lifestyle, environment, and risk of exposure to certain diseases. These vaccines are not necessary for all dogs but may be important for dogs that are frequently exposed to other dogs or certain environments. Examples of non-core vaccines for dogs include parainfluenza and bordetella.

Common Dog Vaccines and Their Purposes
- Rabies Vaccine: This vaccine is required by law in most states and is essential for protecting dogs from the deadly rabies virus. Rabies is a zoonotic disease that can be transmitted to humans, making it a public health concern as well.
- Distemper Vaccine: This vaccine protects against a highly contagious virus that can cause respiratory, gastrointestinal, and neurological symptoms in dogs. Distemper is a serious disease that can be fatal, especially in puppies.
- Parvo Vaccine: This vaccine protects against the highly contagious parvovirus, which can cause severe vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration in dogs. Parvo is most common in puppies and unvaccinated dogs.
- Adenovirus Vaccine: This vaccine protects against two types of adenoviruses that can cause respiratory and liver infections in dogs. Adenovirus type 2 is also a component of the kennel cough vaccine.
- Parainfluenza Vaccine: This vaccine protects against a virus that is one of the causes of kennel cough, a highly contagious respiratory infection in dogs.
- Bordetella Vaccine: This vaccine protects against another cause of kennel cough, the bacterium Bordetella bronchiseptica. It is recommended for dogs that frequently interact with other dogs in settings such as boarding facilities, dog parks, and grooming salons.
In conclusion, dog vaccinations are an essential part of keeping pets healthy and protected from various diseases. Pet owners should work closely with their veterinarian to determine which vaccines are necessary for their dog based on their lifestyle, environment, and risk of exposure to certain diseases.
Vaccination Schedule and Requirements
Puppy Vaccination Schedule
Puppies require a series of vaccinations to protect them from various diseases. The initial vaccination is usually given at 6 to 8 weeks of age, followed by boosters every 3 to 4 weeks until they are 16 weeks old. The typical puppy vaccination schedule includes shots for distemper, parvovirus, hepatitis, and rabies. It is important to note that some vaccines may be required more frequently depending on the dog's lifestyle and risk factors.
Adult Dog Booster Shots
After the initial puppy vaccinations, dogs require booster shots to maintain immunity. The frequency of booster shots depends on the vaccine and the dog's lifestyle. Most adult dogs require a booster shot for distemper and parvovirus every 3 years. Rabies booster shots are typically required every 1 to 3 years, depending on local laws.
Legal Vaccination Requirements
In most states, dogs are required by law to be vaccinated against rabies. The frequency of rabies vaccination varies by state, but most require a booster shot every 1 to 3 years. Some states also require vaccination against other diseases, such as distemper and parvovirus. It is important to check with your local animal control agency or veterinarian to ensure that your dog is up-to-date on all legally required vaccinations.
Overall, vaccination is an important aspect of responsible dog ownership. Proper vaccination can protect your dog from serious and potentially fatal diseases, as well as prevent the spread of disease to other dogs and humans. It is important to work with a veterinarian to develop a vaccination schedule that is tailored to your dog's individual needs and lifestyle.
Costs of Dog Vaccinations
Vaccinations are an essential part of maintaining a dog's health and preventing the spread of diseases. However, the cost of vaccinations can vary depending on several factors. In this section, we will explore the factors that affect vaccination costs, the average cost of vaccinations, and how pet insurance and vaccination coverage can help with these costs.
Factors Affecting Vaccination Cost
Several factors can affect the cost of dog vaccinations, including the type of vaccine, the location of the clinic, and the dog's age and health status. Some vaccines require multiple doses, which can increase the overall cost. Additionally, some clinics may charge more for vaccinations due to their location or reputation.
Average Cost of Vaccinations
The cost of dog vaccinations can vary depending on the factors mentioned above. On average, a basic vaccination package, which includes the core vaccines for dogs, can cost between $20 and $70 per visit. However, if a dog requires additional vaccines or booster shots, the cost can increase. Some low-cost vaccination clinics may offer vaccinations at a lower price, but it is important to ensure that the clinic is reputable and provides quality care.

Pet Insurance and Vaccination Coverage
Pet insurance plans and wellness plans can help with the cost of dog vaccinations. Some pet insurance plans include vaccination coverage, which can cover the cost of vaccinations up to a certain amount. Wellness plans may also include vaccinations as part of their preventative care services. It is important to review the terms of the plan to ensure that vaccinations are covered and to understand any limitations or exclusions.
In conclusion, the cost of dog vaccinations can vary depending on several factors, including the type of vaccine, the location of the clinic, and the dog's age and health status. While some low-cost vaccination clinics may offer vaccinations at a lower price, it is important to ensure that the clinic is reputable and provides quality care. Pet insurance plans and wellness plans can also help with the cost of vaccinations, but it is important to review the terms of the plan to understand any limitations or exclusions.
Health Risks and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases
Vaccinations are an essential part of a dog's health care routine. They help protect dogs from various diseases that can cause severe illness or even death. Here are some of the most common vaccine-preventable diseases that dogs may face:
Canine Distemper and Parvovirus
Canine distemper and parvovirus are highly contagious viral diseases that can be fatal if left untreated. They affect the respiratory and digestive systems, causing symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, and abdominal pain. Dogs can contract these diseases through direct contact with infected animals or their bodily fluids.
Rabies and Leptospirosis
Rabies and leptospirosis are both bacterial infections that can be transmitted to dogs through contact with infected animals or contaminated soil or water. Rabies is a viral disease that affects the nervous system and can cause paralysis and death. Leptospirosis affects the liver and kidneys and can cause fever, vomiting, dehydration, and even organ failure.
Kennel Cough and Other Respiratory Infections
Kennel cough and other respiratory infections are highly contagious viral and bacterial diseases that affect the respiratory system, particularly the lungs. They can cause coughing, sneezing, and nasal discharge, and can lead to pneumonia if left untreated. Dogs can contract these diseases through direct contact with infected animals or contaminated surfaces.
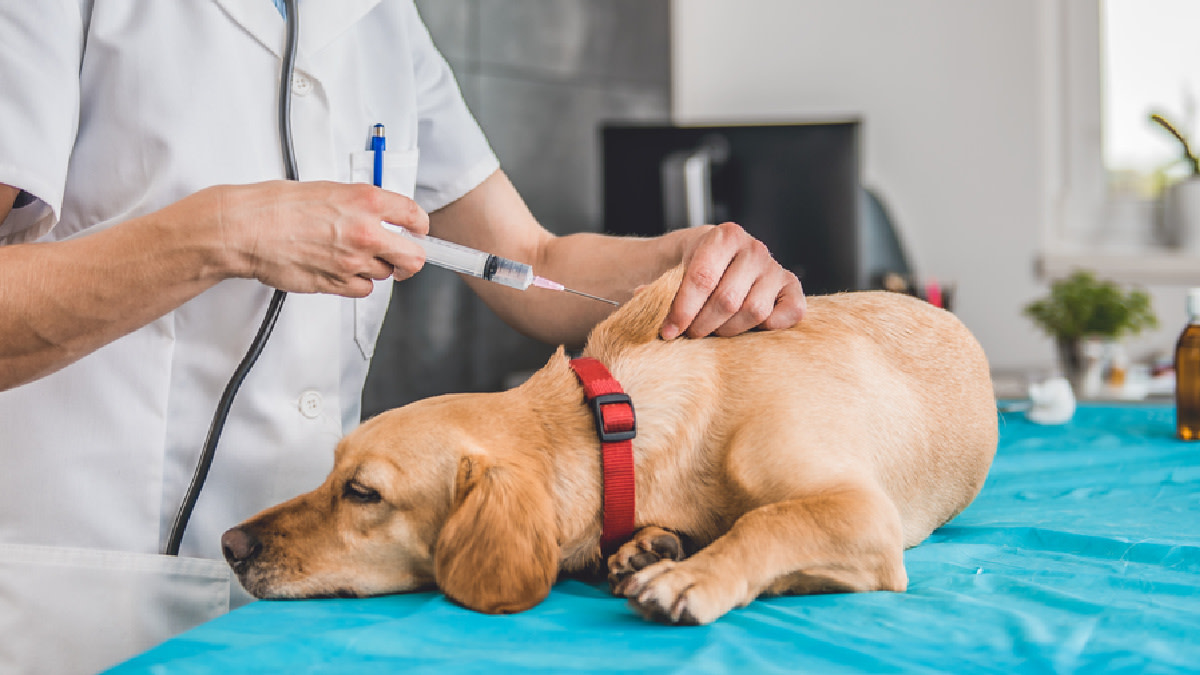
Vaccinations can help protect dogs from these and other infectious diseases. It is essential to follow a vaccination schedule recommended by a veterinarian to ensure that your dog is adequately protected. Regular checkups and vaccinations can help keep your dog healthy and prevent the spread of infectious diseases.
Vaccine Safety and Side Effects
Vaccinations are an important part of keeping dogs healthy and protected from various diseases. However, as with any medical procedure, there are potential side effects to be aware of. It's important for dog owners to understand the risks and benefits of vaccinations and to work closely with their veterinarian to ensure their pet's safety.
Common Side Effects of Vaccinations
Most dogs experience little to no side effects from vaccinations. However, some dogs may experience mild symptoms such as lethargy, decreased appetite, or a slight fever for a day or two after receiving a vaccine. These symptoms are generally mild and resolve on their own without treatment.
Less commonly, dogs may experience more severe side effects such as an allergic reaction. Signs of an allergic reaction can include difficulty breathing, facial swelling, vomiting, diarrhea, or collapse. If your dog experiences any of these symptoms, it's important to contact your veterinarian immediately.
Managing and Reporting Severe Reactions
In rare cases, dogs may experience a severe reaction to a vaccine that requires immediate medical attention. If your dog experiences any of the following symptoms after receiving a vaccine, contact your veterinarian immediately:
- Hives or severe itching
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the face, lips, or tongue
- Collapse or loss of consciousness
It's important to report any severe reactions to your veterinarian and to the vaccine manufacturer. This helps to ensure that the vaccine is safe for other dogs and can help prevent future adverse reactions.
In conclusion, while vaccinations are generally safe and effective, it's important for dog owners to be aware of potential side effects and to work closely with their veterinarian to ensure their pet's safety. By closely monitoring your dog after receiving a vaccine and reporting any adverse reactions, you can help to ensure that your pet stays healthy and protected.
Additional Preventative Care

Heartworm Prevention and Flea/Tick Control
Preventing heartworm and controlling flea and tick infestations are crucial parts of a dog's preventative care. Heartworm is a serious and potentially fatal disease caused by parasitic worms that live in the heart and lungs of infected dogs. Fleas and ticks can transmit diseases and cause discomfort and skin irritation.
There are various preventative products available for heartworm, flea, and tick control. Some of the most common products include chewable tablets, topical treatments, and collars. These products should be used as directed by a veterinarian to ensure their effectiveness.
Routine Health Screenings and Exams
Routine health screenings and exams are also important for maintaining a dog's overall health. These screenings can include fecal exams to check for intestinal parasites, as well as blood tests to check for heartworm and other diseases.
Regular physical exams with a veterinarian can also help identify potential health issues before they become serious. During these exams, a veterinarian will check a dog's overall health, including their teeth, ears, eyes, and body condition.
By following a regular preventative care routine, dog owners can help ensure their furry friends live long and healthy lives. It is recommended to consult with a veterinarian to determine the best preventative care plan for each individual dog.
Choosing the Right Veterinarian and Clinic
When it comes to your furry friend's health, choosing the right veterinarian and clinic is crucial. Here are some factors to consider when selecting a vet and the benefits of regular veterinary care.
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Vet
- Location: Choose a vet that is conveniently located, so you can easily schedule appointments and get there in case of an emergency.
- Services Offered: Look for a vet that offers a wide range of services, including routine check-ups, vaccinations, and emergency care.
- Experience: Choose a vet with experience in treating your pet's specific breed and health issues.
- Cost: Consider the cost of veterinary care and make sure it fits within your budget.
- Reputation: Read reviews and ask for recommendations from friends and family to find a reputable vet.
Benefits of Regular Veterinary Care
- Early Detection of Health Issues: Regular check-ups can help detect health issues early, before they become more serious and expensive to treat.
- Preventative Care: Vaccinations and preventative care can help keep your pet healthy and prevent diseases.
- Longevity: Regular veterinary care can help extend your pet's lifespan and improve their quality of life.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing your pet is healthy and receiving proper care can give you peace of mind and reduce stress.
By considering these factors and the benefits of regular veterinary care, you can make an informed decision when selecting a veterinarian and clinic for your furry friend.
Conclusion
In conclusion, responsible dog ownership encompasses a comprehensive approach to healthcare, with vaccinations playing a pivotal role. These immunizations safeguard not only the well-being of our canine companions by preventing a range of potentially fatal diseases but also contribute to public health by controlling the spread of infectious diseases. The costs associated with vaccinations, while variable, are an investment in your dog's long-term health and should be factored into the overall cost of pet ownership.
Moreover, the article underscores the importance of preventative care, including heartworm, flea, and tick prevention, as well as the significance of routine health screenings and veterinary exams to ensure the optimal health and longevity of our pets. Selecting the right veterinarian and clinic is crucial, as it ensures your dog receives the best possible care tailored to their specific needs.
Ultimately, the key to a healthy and happy pet lies in the partnership between pet owners and veterinarians, emphasizing the importance of regular check-ups, vaccinations, and a proactive approach to health management. This comprehensive care approach not only enhances the quality of life for our furry friends but also fortifies the bond we share with them, making the journey of pet ownership both rewarding and fulfilling.
FAQs
- What are the core vaccines every dog should receive?
- Core vaccines are essential for all dogs as they protect against diseases that are widespread, highly contagious, and pose a high risk of severe illness or death. The core vaccines for dogs include rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and adenovirus.
- How much do dog vaccinations typically cost?
- The cost of dog vaccinations can vary widely depending on factors such as the type of vaccine, the location of the clinic, and the dog's age and health status. On average, basic vaccination packages can range from $20 to $70 per visit, but costs can increase if additional vaccines or booster shots are needed.
- Are there any side effects of dog vaccinations I should be aware of?
- While most dogs experience little to no side effects from vaccinations, some may exhibit mild symptoms like lethargy, decreased appetite, or a slight fever. More severe reactions, although rare, can include allergic reactions such as difficulty breathing, facial swelling, or collapse. It's important to monitor your dog after vaccination and consult your veterinarian if you notice any concerning symptoms.
- What is the recommended vaccination schedule for puppies and adult dogs?
- Puppies require a series of vaccinations starting at 6 to 8 weeks of age, with boosters every 3 to 4 weeks until they are 16 weeks old, covering diseases like distemper, parvovirus, and rabies. Adult dogs typically need booster shots for core vaccines every 3 years, and rabies boosters as required by local laws, usually every 1 to 3 years.
- Why is it important to consult with a veterinarian about my dog's vaccinations?
- Consulting with a veterinarian is crucial because they can provide personalized advice based on your dog's specific health needs, lifestyle, and risk factors. Veterinarians can help determine which vaccines are necessary, establish a vaccination schedule, and ensure your dog is protected against diseases while minimizing the risk of over-vaccination.